N-butyl methacrylate (n-BMA) is a versatile, plasticizing methacrylate monomer used in the production of homopolymers, copolymers and products that we see and use in everyday life.
As a homopolymer, we see poly (n-BMA) used in adhesives and as a polymeric plasticizer for harder resins. Copolymer applications include water-borne industrial and architectural paints, textiles, paper & leather coatings, wood coatings, adhesives, inks, caulks, and sealants. N-BMA also demonstrates flexibility, durability, UV, and moisture resistance in exterior decorative paints and automotive finishes.
In solvent based systems, it improves solubility of the copolymer resin. Copolymers with methyl methacrylate (MMA), exhibit enhanced flexibility and toughness without the need for a plasticizer.Take a look at the chemical structure of this unique building block monomer below.

Physical Properties of n-BMA
N-butyl methacrylate is a clear, colorless liquid with a faint ester-like odor. The chart below summarizes the physical properties of n-BMA and relevant regulatory information.
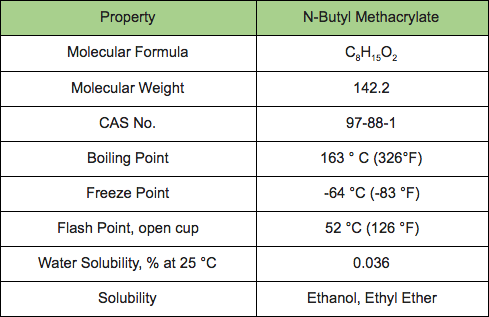
N-BMA is classified as hazardous (flammable, skin irritant, sensitizing and toxic/harmful to aquatic life), but the chemical industry has handled it safely for more than 80 years. The use of n-BMA in methacrylate polymers dates back to the work of Otto Rohm and others in the 1920s. N-BMA is of low concern to human health and the environment.
NFPA Rating:
| Hazard | Value | Description |
| Health | 1 | Can cause significant irritation |
| Flammability | 2 | Must be moderately heated or exposed to relatively high ambient temperatures before ignition can occur |
| Instability | 2 | Readily undergoes violent chemical changes at elevated temperatures and pressures |
An excellent industry publication covering the environmental, health, safety, and regulatoryaspects of n-BMA includes the recommended storage life of methacrylate monomers (one year, when following recommended handling and storage guidelines).
Attributes of n-BMA
The n-BMA monomer imparts a distinct combination of properties associated with high quality paint and coatings. Attributes contributed by n-BMA include the following:
- Weatherability and UV resistance
- Transparency and non-yellowing characteristics
- Flexibility, toughness, and durability
- Compatibility with a wide variety of resin systems and solvents
- Adhesion to a wide variety of substrates
Applications of n-BMA
N-butyl methacrylate (n-BMA) is used in both homopolymer and copolymer compositions. End-use markets include inks, copier toners, adhesives, exterior architectural and industrial paints, over-paint varnishes, automotive finishes and lacquers, wood coatings, floor polishes, paper and leather coatings, and textile binders. We also see n-BMA used to produce acrylic copolymers used in molding and sheet extrusion and clear plastic parts. N-BMA contributes flexibility, durability, moisture, and UV/weathering resistance. It is often copolymerized with methyl methacrylate where it contributes flexibility and improved toughness to polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), superior transparency and high gloss, and fast dissolution in solvents. Copolymerization into PMMA can improve toughness without the incorporation of plasticizers that detract from UV/weathering resistance.
The poly(n-BMA) homopolymer has a glass transition temperature at + 20 percent. It exhibits tensile strengths of about 500 psi and elongations of 300 percent and above. Poly(n-BMA) is used as a plasticizer for harder resins and an adhesion promoter. The homopolymer is compatible with PVC resins, epoxy and alkyd resins, cellulosic acetate butyrate and nitrocellulose, and rosin ester resins. The homopolymer is added to harder resin systems to increase toughness, flexibility, adhesion, durability, and softness. Because PMMA generally needs to be plasticized, plasticization with the homopolymer poly(n-BMA) would show better outdoor weathering characteristics versus other types of plasticizers. Poly(n-BMA) shows good resistance to yellowing.
In ink applications, n-BMA based resins enhance substrate adhesion, pigment dispersion, flexibility, and toughness. As a binder, n-BMA homo and copolymers are used in a flexographic, gravure, and screen printing.
N-BMA is used in both clear and pigmented coatings where it contributes clarity, flexibility and durability. Copolymers with MMA are used in coatings for plastics, sealers for concrete, high solids coatings and ink formulations. Processors can achieve a good balance between hardness and flexibility with the proper selection of MMA & n-MBA comonomer ratios.
Homopolymers, and copolymers with iso-butyl methacrylate, are soluble in a wide variety of solvents, including mild solvents such as petroleum distillates and n-propanol. Coating technologies include water-borne, solvent based, suspension polymerization, powder coatings, and UV/EB cured coatings.
In adhesives, n-BMA is a comonomer used for thermosetting adhesives and pressure sensitive adhesives. The reactive thermosetting systems are normally based on MMA and n-BMA monomers, plus other comonomers. These are two-part systems applied in a thin bond line and cured, affording tough bonds on a wide variety of substrates with medium-to-high peel and shear strength. The cure component is a peroxide or hydroperoxide, whereas the monomer component contains accelerators and toughening additives. Applications are in assembly bonding operations.
N-BMA and Glass Transition Temperature of Acrylic Monomers
The Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) of the homopolymer poly (n-BMA) is 20 °C. In random copolymers, we can estimate the Tg by using the weight fraction of the different monomers and their Tg values for the homopolymer. This method assumes that the repeat unit of the copolymer can be divided into weighted additive contributions to the Tg that are independent of their neighbors. The chart below provides reference Tg values based on the homopolymers of these key monomers.
Homopolymer glass transition temperatures, Tg (◦C), for various acrylate monomers:
| Monomer | Tg (◦C) |
| MMA | 105 |
| Styrene | 100 |
| Ethyl Methacrylate | 66 |
| iso-Butyl Methacrylate | 50 |
| N-Butyl Methacrylate | 20 |
| Vinyl Acetate Monomer | 30 |
| Glacial Acrylic Acid | 87 |
| Butyl Acrylate | -45 |
| 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate | -65 |
For a discussion on estimating the Tg of random copolymers please see this link.
FDA Listings for n-BMA
The United States Food and Drug Administration cites homopolymers and copolymers of N-BMA in the following federal regulation codes (CFRs) covering indirect use in food contact applications such as adhesives, coatings and packaging.
Regulations in 21 CFR:
| 175.105 | 177.1010 |
| 175.300 | 177.1200 |
| 175.320 | 177.1630 |
| 176.170 | 177.2420 |
| 176.180 | 177.3790 |
Purchasing High-Purity n-Butyl Methacrylate
If you are looking to purchase high-purity n-BMA, Gantrade Corporation markets this monomer in 20 MT (44,000 lb.) ISO Tanks and in 200 Kg. factory-sealed drums for industrial use only.
The purity of our n-BMA is greater than 99.5 percent. Gantrade’s n-BMA contains 50-100 ppm of MEHQ inhibitor. Take a look at Gantrade’s n-BMA sales specifications in the chart below.
%20specs.png?width=555&name=n-butyl%20methacrylate%20(n-bma)%20specs.png)
At Gantrade Corporation, we offer a broad line of high-quality products serviced by knowledgeable professionals. Contact us today for a consultation to discuss your needs for n-BMA and other chemical products.